Optical element
Mirrors are the most commonly used optical components in optical laboratories and optical instruments. SIMTRUM provides metal mirrors and dielectric film mirrors with low thermal expansion coefficient, high-quality surface accuracy (λ / 10), and high-quality surface quality (15-5). This article introduces the principles of Fresnel equations, metal mirrors, dielectric film mirrors, and the optical mirror products of Optics Technology.
Fresnel equation
French physicist Fresnel (yes, the man that invented the Fresnel lens) uses wave optics theory to explain the reflection and refraction properties of light propagating at the interface of different media.
Light can be represented by any set of orthogonally polarized electromagnetic waves. The Fresnel equation decomposes light into s-polarized light and p-polarized light. The boundary conditions of the electromagnetic theory are used to solve for reflection and transmittance.
For s-polarized light (TE mode) propagating at the interface of the medium, there are the following electromagnetic field boundary conditions:
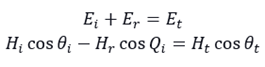
For the propagation of p-polarized light (TM mode) at the interface of the medium, there are the following electromagnetic field boundary conditions:
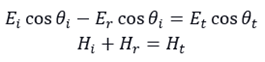
It could get the solution of the amplitude reflection coefficient and amplitude transmission coefficient of s-polarized light and p-polarized light:
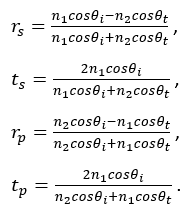
The amplitude reflection coefficient and amplitude transmission coefficient are functions of the angle of incidence (AOI) and refractive index. The optical sparse medium enters the optically dense medium (n1 <n2) and the optically dense medium enters the optical sparse medium (n1> n2). The equations are different, as shown in the following figure.
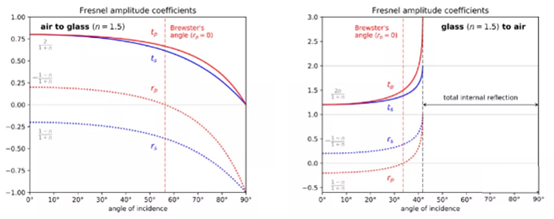
For a light sparse medium entering an optically dense medium, the amplitude transmission coefficient decreases with increasing angle of incidence, while relatively, the amplitude reflection coefficient increases with increasing angle of incidence.
For the case where light enters the optically dense medium from the optically dense medium when the incident angle is greater than the critical angle arcsin (n2 / n1), a "Total Internal Reflection" phenomenon occurs.
Optical fiber is to achieve long-distance optical communication, by use of the principle of total reflection. We are entering the Era of All-optical Interconnection! It is reported that Huawei has already released the Zhijian all-optical network strategy for the F5G era. It has introduced 10G PON, Wi-Fi 6, eAI ONT, 200G / 400G, Liquid OTN, and other innovative technologies and products, focusing on the four major constantly innovating scenarios of "all-optical transmission, all-optical access, all-optical data center, and all-optical park”!
When the angle of incidence is perpendicular to the angle of refraction (Brewster angle), the reflection coefficient of p-polarized light is 0. At this time, the reflected light has only s-polarized light, resulting in full polarization. Using this principle, the "sheet stack" can be used to obtain polarized light from natural light; Brewster windows are used in laser resonators.
For transmitted light, the transmission coefficient is always positive, indicating that the phase of the refracted light and the incident light are always the same, and there is no phase change. For reflected light, there are two cases of "optical sparse medium incident optical dense medium (n1 <n2)" and "optical dense medium incident optical dense medium (n1> n2)", "incident angle> Brewster angle" and "incident In the case of angle <Brewster angle, s-polarized and p-polarized light may produce "half-wave loss".
The reflectance and transmittance can be calculated by the following formula:
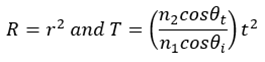
Therefore, the reflectivity of s-polarized light and p-polarized light is:
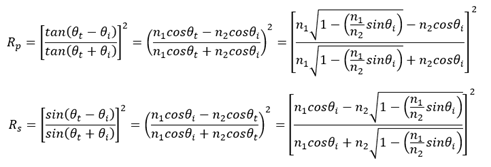
When the incident ray is near normal, the reflectance and transmittance are:
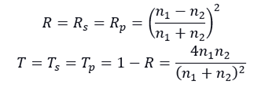
The reflectance and transmittance curves of s-polarized light and p-polarized light are shown in the figure below for two cases: light incident medium and light dense medium (n1 <n2) and light dense medium (n1> n2)

The Fresnel reflection equation explains this phenomenon well: under normal incidence, the reflectivity of the water surface is not high, but under grazing incidence, a strong specular reflection is formed!
Principle of Metal Mirror
Mirrors are often coated with gold, silver, and aluminium metal films. Why is the reflectivity of metals so high? Metals have a complex refractive index:
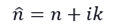
Therefore, for metal media, the form of Maxwell's equations is different from that of dielectric media. Considering the case where the air is incident on a metal mirror, the refractive index of the metal is brought into:
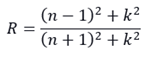
The refractive index of metals such as gold and silver in the visible to the near-infrared band is shown in the figure below. In fact, the part is close to 0, and the imaginary part is very large, so the metal has a high reflectivity in these bands and is often used to make mirrors.
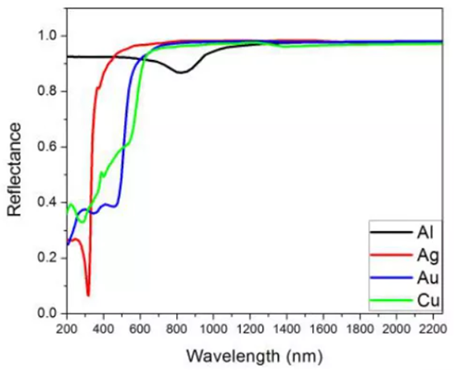
The reflectance spectra of common metals are as follows:
Dielectric film mirror
Due to a certain loss of the metal itself, the reflectivity of the metal mirror can only reach 99% or less. In high-power laser applications, the Dielectric mirror & Bragg mirror is often used as a reflector. Multilayer dielectric film can realize the constructive interference of reflected light. It is to realize the interference of reflected light to achieve ultra-high reflectivity (even up to 99.999%) and eliminate the thermal effects caused by mirror damage.
References:
[1] E. Hecht, 2002, Optics, 4th Ed., Addison Wesley
[2] 郁道银,谈恒英,工程光学,机械工业出版社
[3] Max Born, Emil Wolf, 光学原理,第七版,电子工业出版社
[4] Wikipedia contributors. (2020, May 19). Fresnel equations. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 11:56, May 24, 2020, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Fresnel_equations&oldid=957525235
[5]维基百科编者. 菲涅耳方程[G/OL]. 维基百科, 2019(20190905)[2019-09-05]. https://zh.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=%E8%8F%B2%E6%B6%85%E8%80%B3%E6%96%B9%E7%A8%8B&oldid=55967376.